 | Central Vascular Clinic | | 趙啟明醫生醫務所 Dr. Leo K.M. CHIU |
|  |
|
|
|
|  |
What are the options of access?
|
Permanent Accesses
|
|
What is haemodialysis access?
When kidneys fail to work blood has to be cleaned by a process known as “haemodialysis” (HD). In HD, blood is taken to the artificial kidney for filtration of wastes and removal of excess fluid from the body. Cleaned blood is then pumped back to the bloodstream. A passage to safely remove and return blood (vascular access) 2 to 3 times a week is necessary. A good access maintains a strong blood flow to provide adequate dialysis and improve the quality of life.
What are the options of haemodialysis access?
Most of the time renal failure is a chronic problem and requires long-term dialysis. Permanent access is therefore necessary. Among the two types of permanent access, arteriovenous fistula is preferred. Temporary access is good for short term dialysis or is for emergency situation before permanent access is ready for use.
There are two types of permanent accesses; arteriovenous fistula and arteriovenous graft.
Permanent Accesses
.jpg)
Arteriovenous Fistula (AVF)
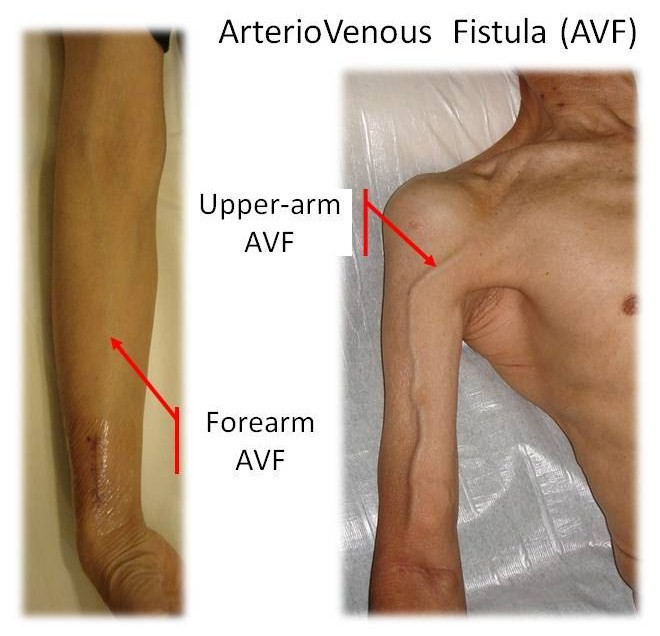
- Arteriovenous fistula is often constructed on an outpatient basis.
- Ultrasound “mapping” helps to select the best veins for a fistula.
- Under local anaesthesia, an arteriovenous fistula is made by directly connecting an artery to a superficial vein usually in the forearm.
- After a few weeks of maturation, the vein becomes larger and stronger.
- The strong arterial blood flow allow then for adequate dialysis.
- Since the veins are close to the surface, the new access is easy to reach and repeated needle insertions becomes possible
Arteriovenous Graft (AVG)
- Ateriovenous grafts is formed through the indirect connection of the artery to a vein by a synthetic small flexible tube (Graft) under the skin.
How to choose between the two types of permanent access?
- Arteriovenous fistula is the preferred vascular access, for following reasons: (1) Veins and arteries are part of the body so a fistula is less prone to infections or blood clots than other types of access. (2) It self-heal after needle stick, so a fistula can last a long time.
- Grafts are used when patients have small vein that cannot develop into a suitable fistula. Grafts are the second-best access. Compared to a AVF, a graft is more likely to: (1) Become infected and/or clotted, because the synthetic material is foreign to the body.(2) Develop holes, because the synthetic material does not self-heal after needle punctures
Temporary Access
_.jpg)
Central venous catheters
- Catheters are most commonly used as a temporary access for a few weeks.
- Catheters are flexible, hollow tubes which allow blood to flow in and out of your body.
- It is inserted either in the neck, chest, or groin, into a “central” vein. The other end of the tubing is outside the skin and used for hooking up to the dialysis machine.
- A catheter can be used right away for dialysis while waiting for a fistula or graft to mature.
- The catheter is the poorest option for long term dialysis: (1) It extends outside of the body, so it is the most prone to infection. (2)Blood flow rates are often poor, and it is hard to get enough dialysis. (3) Catheters are very likely to clot. (4) It can cause clotting of the central vein and make the arm vessels impossible to be used for dialysis later.
|
|
|
|
|
|